The alternator is a critical component in a vehicle that’s responsible for charging the battery and supplying power to the car’s electrical system while the engine is running. It achieves this by converting mechanical energy, usually from the engine’s rotation via a belt, into electrical energy through a process called magnetic induction.
What is Alternator Fuse ?
In many vehicles, there’s a high-amperage fuse or a fusible link situated between the alternator’s battery terminal and the actual battery. Additionally, there are often low-amperage fuses connected in series with the alternator’s sense terminal and ignition terminal.
Where is the Alternator Fuse Located?
The location of both the high-amperage and low-amperage alternator fuses differs based on the specific make and model of the vehicle. Usually, the high-amperage fuse for the alternator is situated under the hood near the battery terminal or directly on the battery itself.
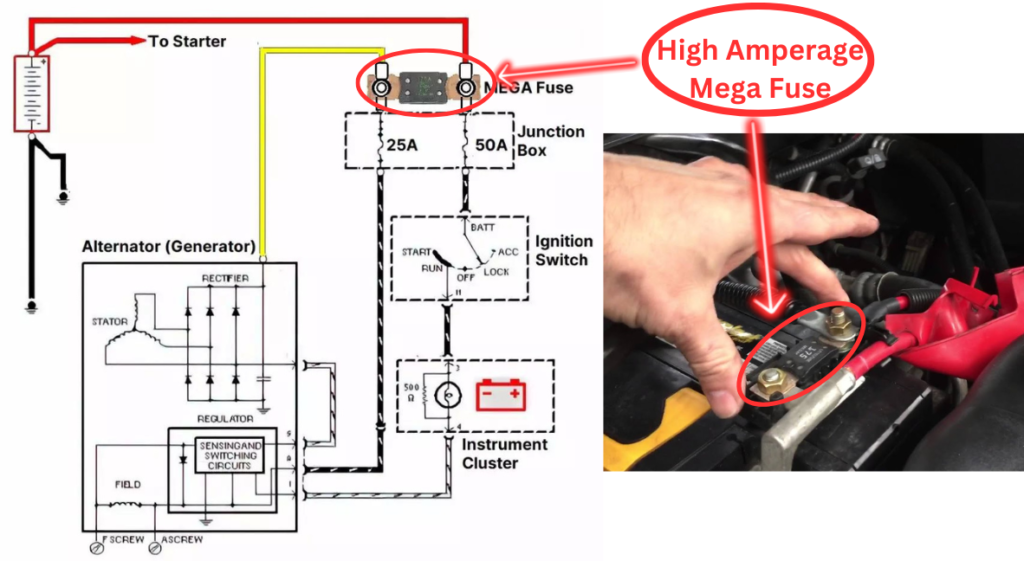
The low-amperage fuse is typically found within the fuse box, and its location varies depending on the specific make and model of the car. To locate the fuse box, refer to the owner’s manual. Once you’ve located the fuse box, refer to the fuse box diagram to identify the specific fuse allocated for the alternator.
What is the Function of Alternator Fuse ?
The alternator fuse, similar to other fuses, serves as a circuit protection mechanism. Its primary role is to blow when there’s an excess of current flowing through, preventing a circuit overload. This action helps avoid scenarios like melted wires, harm to components, and the risk of a potential fire.
Specifically, the high-amperage fuse is designed to safeguard the battery and the alternator from excessive current flow. On the other hand, the low-amperage fuse is dedicated to shielding the voltage regulation circuit within the alternator.
If any of these fuses blows, it can disrupt the proper functioning of the battery charging circuit, potentially leading to issues with the charging system and electrical components in the vehicle.
How to Tell if an Alternator Fuse is Blown?
To check if the alternator fuse is blown, start by examining the symptoms: if the battery warning light on the dashboard is illuminated, lights appear dim or flicker, the battery is dead, or there are issues with power windows, it could signal a problem in the battery charging system.
The most common issue causing charging problems is a blown fuse. If you’ve noticed any of these signs, locate the fuse box and visually inspect the alternator fuse. You can also use a Digital Multimeter (DMM) to measure its resistance and confirm if it’s blown.

Can You Drive the Car With Blown Alternator Fuse?
Yes, you can drive the car with a blown alternator fuse. However, driving in this state means running the vehicle without the battery recharging and other electrical systems drawing power without replenishment. It’s recommended to replace the blown fuse promptly. If a spare fuse isn’t available, replace it with a non-essential fuse temporarily.
