What is a Catalytic Convertor?
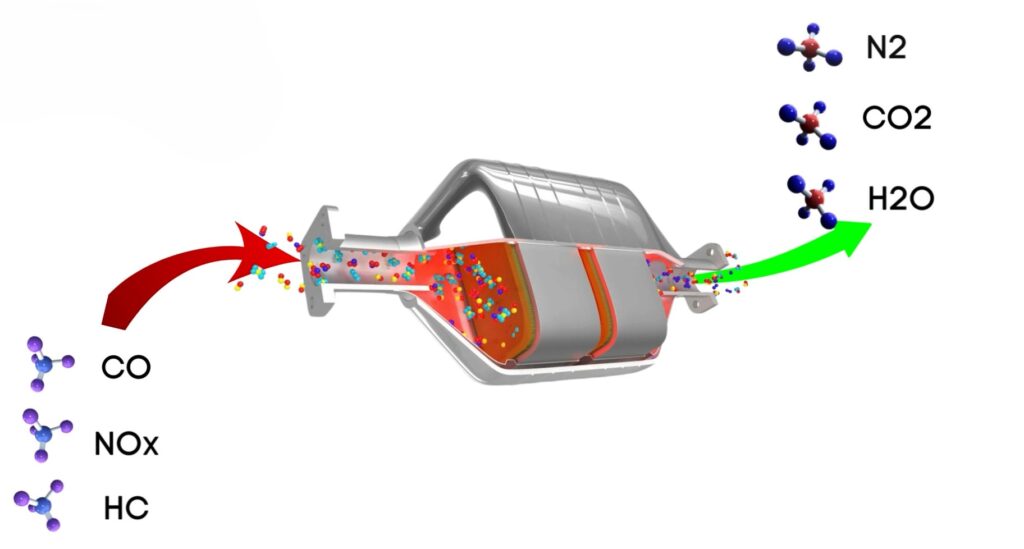
The purpose of a Catalytic Converter is to use a chamber called a catalyst to change the harmful compounds from an engine’s emissions into environmentally safe gases.
When the engine releases harmful gases like carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and hydrocarbons, these gases travel through the catalyst and are converted into safer gases like steam, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen.
Where is Catalytic Converter Located?
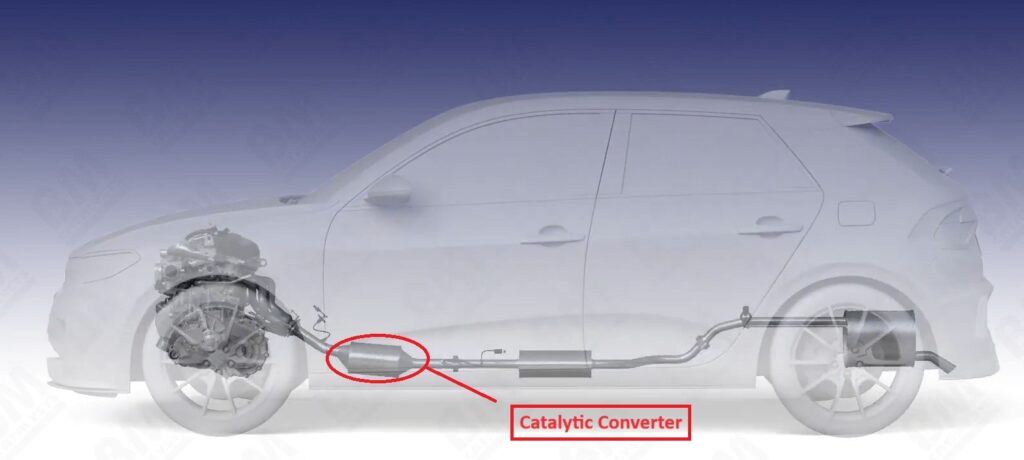
The catalytic converter is located in the exhaust line on the underside of a vehicle, between the engine and the muffler, and looks like a large metal box.

Bad Catalytic Converter Symptoms
A malfunctioning Catalytic Converter can manifest in various symptoms, indicating potential issues with the vehicle’s performance:
- Check Engine Light Comes On: Check Engine Light Comes On. While a check engine light can indicate various problems, a malfunctioning catalytic converter is a frequent trigger. This happens because the engine control unit detects issues related to the catalytic converter and triggers relevant fault codes.
Here are some OBD-II codes related to a bad catalytic converter:- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- P0421: Warm Up Catalyst Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- P0422: Main Catalyst Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- P0423: Heated Catalyst Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- P0424: Heated Catalyst Temperature Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- P0425: Catalyst Temperature Sensor (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
- P0426: Catalyst Temperature Sensor Range/Performance (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
- P0427: Catalyst Temperature Sensor Low (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
- P0428: Catalyst Temperature Sensor High (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
- P0429: Catalyst Heater Control Circuit (Bank 1)
If you want to know the meaning of each OBD-II code, check our database on OBD-II codes.
- Poor Engine Performance: A clogged or damaged catalytic converter can lead to poor engine performance, manifesting as This can manifest as:
- Rough idle
- Hesitation
- Reduced power
- Sluggish acceleration
- Rotten Egg Smell: While you’re driving, if the honeycomb inside the catalytic converter is either broken or clogged, it won’t be able to process the smelly gas called hydrogen sulfide into an odorless gas, resulting in a rotten egg smell.
- Failed Emissions Test: A bad catalytic converter can cause your vehicle to fail an emissions test due to increased levels of harmful gases.
- Rattling Noise: A rattling noise coming from your catalytic converter could be a broken-down honeycomb. This could be due to high temperatures caused by a rich fuel condition.
What Causes the Malfunction of Catalytic Converter?
Causes of a Faulty Catalytic Converter
- Overheated, melted, or broken converters: Any malfunction causing unusually high unburned fuel with high Oxygen levels to enter the converter will dramatically elevate its temperature.
Potential causes for high unburned fuel are:- Misfire
- Low compression
- Air-fuel ratio imbalance
- Poor spark or no spark
- Faulty oxygen sensor
- Catalyst poisoning occurs when the converter is exposed to emissions containing substances that coat the working surfaces, enveloping the catalyst to the point it cannot contact and treat the exhaust.
Potential causes for coated or fouled substrate may include:- Excessive carbon buildup in exhaust
- Internal coolant leaks through head or intake gasket
- Use of non-converter-safe gasket sealants
- Excessive throttling or burn out
- Improper fuels or additives




